2024年2月26日,上海交通大学Bio-X研究院陆青课题组与山东大学生命科学学院徐志刚课题组与北京脑科学与类脑研究所熊巍课题组合作,在PNAS发表了题为Disruption of Cdh23 exon 68 splicing leads to progressive hearing loss in mice by affecting tip-link stability 的研究论文,报道了Cdh23基因可变剪接调控毛细胞顶连接稳定性。

毛细胞是动物内耳中负责感知听觉信息的感受器细胞,将负载声音信息的机械能信号转换为电信号。毛细胞上表面有多根以微丝为骨架的静纤毛(stereocilia),组织成多排高度不同的阶梯状模式。顶连接(tip links)联系了较低排静纤毛顶部与其相邻较高排静纤毛侧部,而机械-电转换(MET)离子通道就位于顶连接下端附近。当静纤毛在声音信号的作用下向较高排的方向偏转时,顶连接张力增加,MET通道开启,阳离子内流,毛细胞去极化,产生感受器电位【1】。
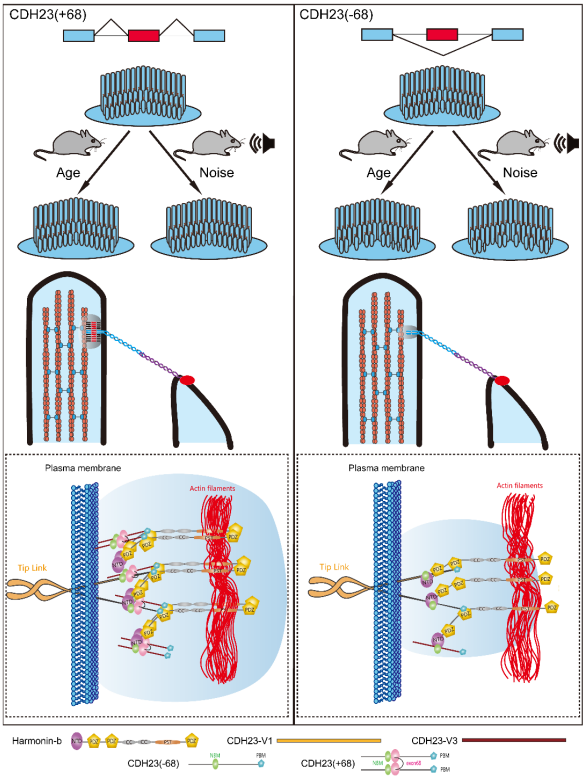
可变基因剪接作为一种重要的转录后加工方式,大大增加了蛋白多样性【2】。尤其是组织/细胞特异性可变基因剪接,在特定组织/细胞的分化或功能执行中发挥了极其重要的作用【3】。研究显示可变基因剪接在听觉系统也发挥了重要作用,其中最为人熟知的是Cdh23基因的可变剪接。Cdh23基因编码一个非典型钙粘蛋白,构成顶连接的上端部分,其胞内段与harmonin等蛋白形成蛋白复合体【4,5】。Cdh23基因含有69个外显子,其中68号外显子受到内耳特异性可变剪接的调控,产生Cdh23(+68)和Cdh23(-68)两种剪接本,其中Cdh23(+68)只在内耳中被检测到【5,6】。68号外显子长105个碱基对,编码位于胞内段的35个氨基酸,其组织特异性可变剪接的调控机制及生理功能一直以来都不十分清楚。研究团队的前期工作显示Cdh23基因可变剪接受到RNA结合蛋白RBM24等的调控,Rbm24基因敲除小鼠耳蜗中Cdh23基因68号外显子可变剪接几乎完全被阻断,表明RBM24是这一可变剪接过程的重要调控因子【7,8】。
山东大学生命科学学院博士后李娜娜、北京脑科学与类脑研究所博士后刘双、上海交通大学硕士毕业生赵丹歌为本论文的并列第一作者,山东大学生命科学学院徐志刚教授、北京脑科学与类脑研究所熊巍研究员、上海交通大学Bio-X研究院陆青研究员为本论文的共同通讯作者。美国霍普金斯大学的Ulrich Müller教授对本文做出了重要贡献。
参考文献
1. Gillespie PG and Müller U. (2009) Mechanotransduction by hair cells: models, molecules, and mechanisms. Cell 139, 33-44.
2. Wang ET, et al. (2008) Alternative isoform regulation in human tissue transcriptomes. Nature 456:470-476.
3. Tapial J, et al. (2017) An atlas of alternative splicing profiles and functional associations reveals new regulatory programs and genes that simultaneously express multiple major isoforms. Genome Res 27:1759-1768.
4. Siemens J, et al. (2002) The Usher syndrome proteins cadherin 23 and harmonin form a complex by means of PDZ-domain interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99, 14946-14951.
5. Siemens J, et al. (2004) Cadherin 23 is a component of the tip link in hair-cell stereocilia. Nature 428, 950-955.
6. Xu Z, Peng AW, Oshima K, Heller S. (2008) MAGI-1, a candidate stereociliary scaffolding protein, associates with the tip-link component Cadherin 23. J Neurosci 28, 11269-11276.
7. Li N, Du H, Ren R, Wang Y, Xu Z. (2020) Alternative splicing of Cdh23 exon 68 is regulated by RBM24, RBM38, and PTBP1. Neural Plast 2020, 8898811.
8. Wang Y, Zhang C, Peng W, Du H, Xi Y, Xu Z. (2023) RBM24 is required for mouse hair cell development through regulating pre-mRNA alternative splicing and mRNA stability. J Cell Physiol 238, 1095-1110.
文章链接:https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2309656121